Substantial changes in a website in the areas that significantly affect the search engine are technically known as website migration. There are several areas that need change when it comes to website migration. The location, structure, content, platform, design, and URL are changed for migration of the website. If done incorrectly, website migration can lead towards revenue and traffic loss for several months. Actually, deep down the migration affects the ranking signals of the search engine. In this blog w will cover several areas necessary for website migration.
Table of Contents
Reasons to use website migration?

There are myriads of reasons why a website owner could choose to migrate a website. Maybe the site owner found a new web hosting company, the company changed locations or rolled out new website deigns on a better platform. First, let us start with the types of website migration connected to changes in the location of site.
- The location of the site changes with URL or without URL
- Change in protocol takes place.
- Changes in subdomain or subfolders when a business moves ccTLD (country code top-level domain) into subfolders or subdomains.
- When rebranding the change occurs in domain name.
- In case of launching international website, the migration occurs from country code top-level domain to generic top-level domain.
- In case of changing the architecture of website the internal link and structure of URL are affected.
The below mentioned changes occur due to the changes in the design, platform, structure and content of the website:
- In case of upgrading the platform the URL and design of the website changes
- The consolidation, pruning and rewriting the content brings changes in the internal linking and navigation of the website.
- In case of moving the website for mobile setup can be the partial migration. The site is replaced by PWA or AMP.
- In case of changing the taxonomy of the website, the structural changes occur.
- Revamping the design of the website will change the media and code.
There are also hybrid migrations apart from the types mentioned above that combine changes. This can get more complex and risky. However, if you plan ahead and execute the migration perfectly then you can run it smoothly.
Let us skim through the necessary steps that are needed to be taken for website migration. There are 5 essential phases of website migration and skipping one of these can create halts.
Plan and Scope Needs

Never take the step without defining crystal clear objectives. Determine the complete set of types of changes. Identify the legacy issues, and critical aspects of the projects. Also determine the ROI (return on investment) and choose the appropriate options. Also prepare scenarios of forecasting for growth and risk. Involve stakeholders and ask for feedback regarding the content, SEO, Analytics and UX. Involve these experts and plan the activities in detail. After this phase you will have a list of prioritized activities. Plan an anticipated date of launch. Avoid launching the site during or ahead of peak time.
Prepare before Launching:

Activities during the under-development phase of website are involved in pre-launch prep. Capture the SEO requirements for the new website and get information on the prototypes and wireframes from designers and architects. Also review all templates that identify the SEO and UX issues before time.
SEO and Site Migration: How are they Connected?
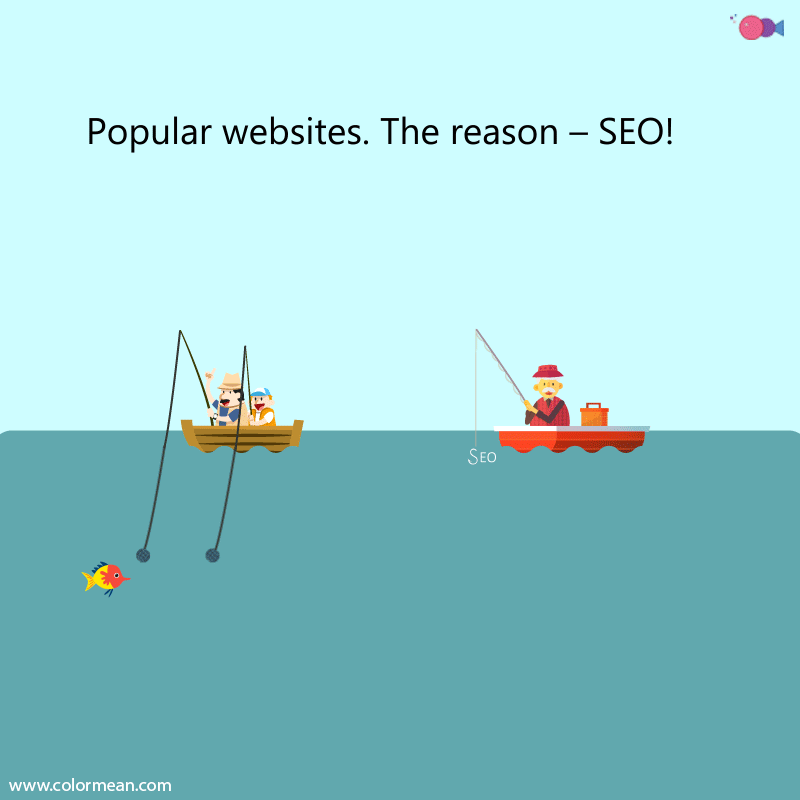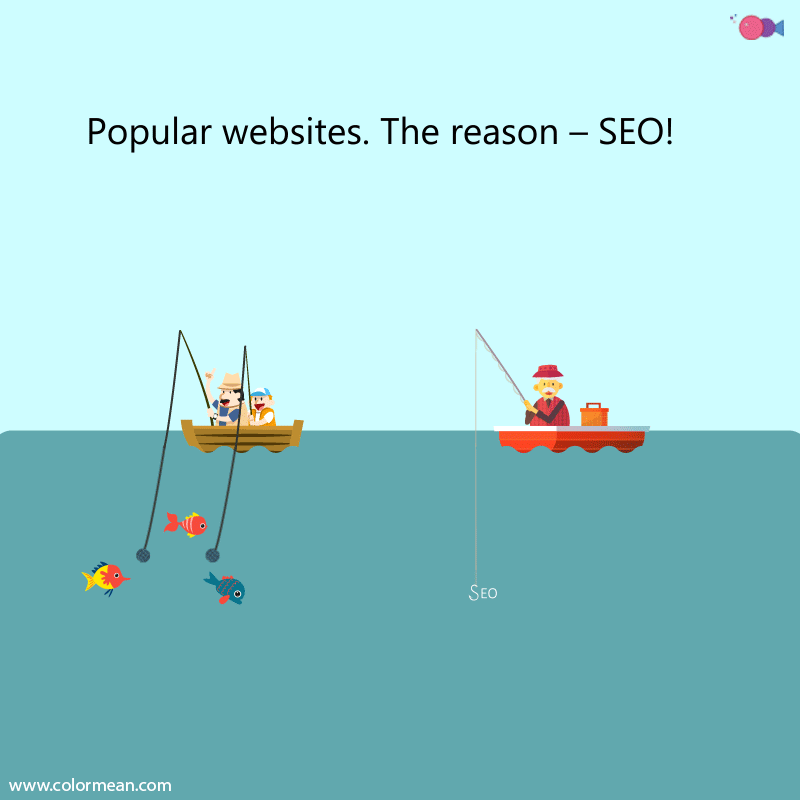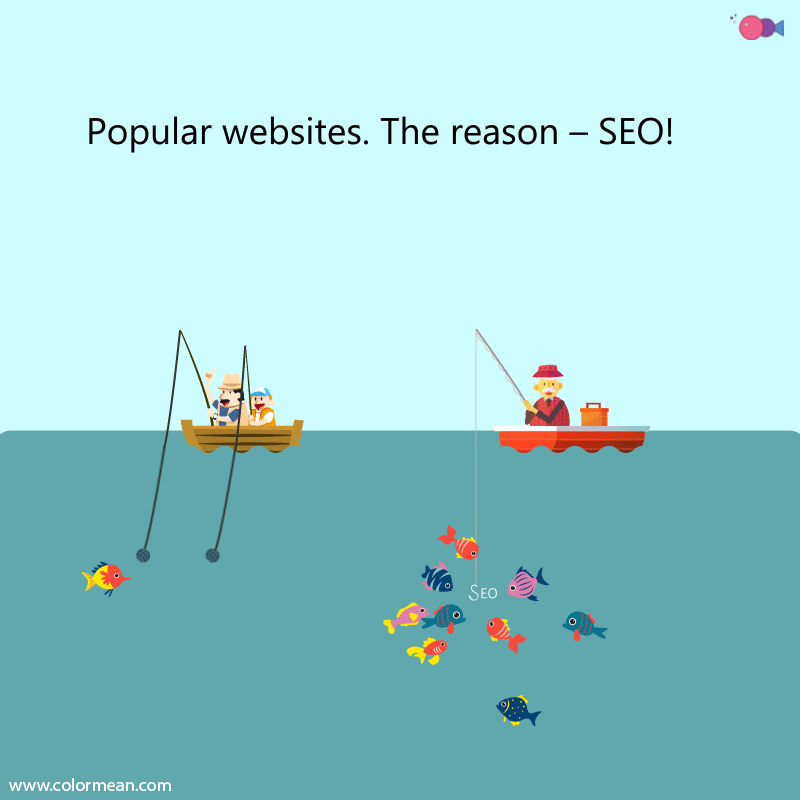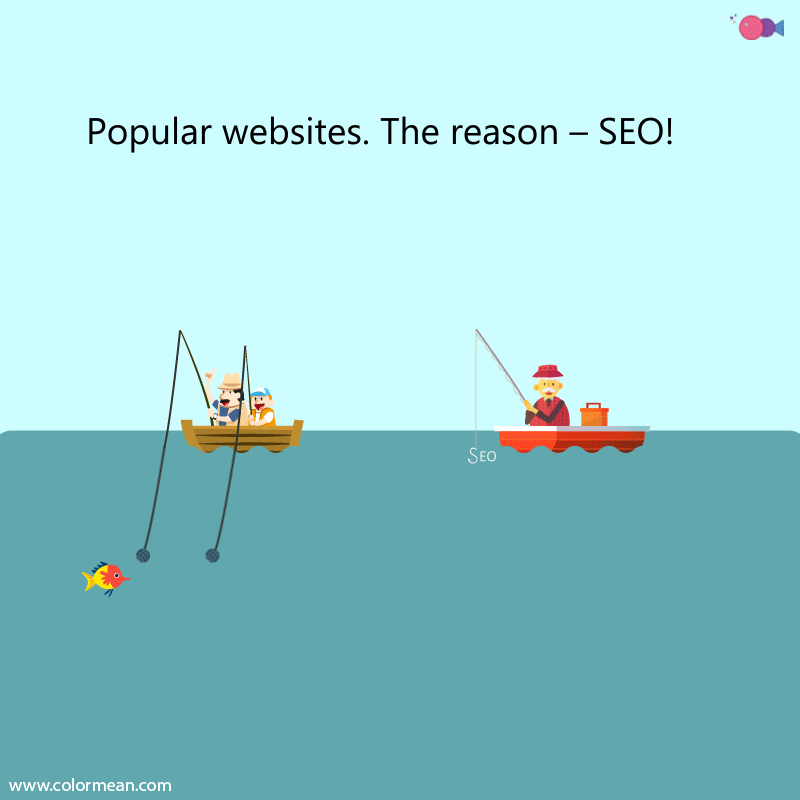
After the review, a set of technical SEO specs have to be documented. These requirements state the SEO requirements in relation to the scope of costs and work of the project. Specs are highly detailed and must be easily convertible. The requirements must cover the structure of URL, structured data, copy and headings, internal linking, HTML site map, mobile setup, redirects, JavaScript, SSL certificate transfer and Custom 404 page. From the CMS perspective the requirements must also include the updating of title pages, meta descriptions, and robots txt files.
Prioritize and Crawl Pages
The quality and quantity of pages determine the success of the migration. When you convert pages well, they will drive the traffic. For prioritizing the pages, identify all the indexable and top performing pages and move slowly the legacy site. After determining all the indexable pages, identify the top performing ones that generate visits, and contribute to the revenue by converting well. Crawling the old site will enable you to copy the URLs, titles of pages, meta data, redirects, headers and broken links as well. Also keep the copy of the crawled data until after you complete the migration process.
Benchmark Your Move
Benchmark the performance of the legacy site near the launch time. Benchmarking lets you compare the performance of new and old sites and also diagnose the underperforming areas. Track the keywords ranking as it will determine whether the migration has taken place smoothly or not. Search the keywords that have represented the site mostly. Ensure that you keep check on keywords that bring traffic to the site. The loading times of the pages of new site has a great impact on the sales and traffic.
15 Tips to Effectively Migrate Your Site
There are some common mistakes that can totally halt the migration process or create problems and the solutions to these problems.
- Avoid unclear and unrealistic goals and strategy they lead to poor implementation.
- The plan must be flexible and include contingencies as well. Avoid seasonal peaks and plan migration only in slow parts of the year.
- The lack of resources or having a limited budget can cause the loss of revenue. Add additional source of 20% to your budget.
- Make decisions from a SEO and UX standpoint. If not, then it will lead to issues in indexing and crawling. The conversations of the site can also be damaged.
- Professional support in the last steps can be risky. Involve professionals from day one.
- Thorough testing is crucial and do not rush the launch. Testing must take place on attest server.
- Ignoring bug fixing can be risky and render technical obstacles.
- Replace and remove links that end to 404 pages, during the migration process.
- Update all internal links. Redirects can reduce the page rank.
- Solve all the issues regarding the duplicate content during the process of migration.
- Identify deleted or removed pages and address the issues.
- Manage the site map for the new migrated site.
- Hold the control on the domain.
- Monitor Referral traffic.
- Last but not least update the profiles and bios on all of the social media, websites, forums, and platforms.
Conclusion
Consider website migration only if it is worthy for your current business and brand. In addition, depending on your hosting service provider you might get free website migration to make the switch easier for you. Otherwise, it can be an extensive venture to take on alone. Finally, before considering site migration be sure to plan ahead, be keen on details, seek professional assistance, and conduct thorough testing and maintenance of analytics on each step of the process.