Working from home is one of the preferred methods to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 so you should be applauded for efforts. But remote workers are tasked with another issue, how to protect themselves from cyber-attacks. When it comes to cyber risks, prevention is better than the cure. So today we’re examining 3 must-have tools to make you virtually immune from cyber threats. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
1. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Usually in the office workers are connected to each other and that one printer via a Wide Area Network (WAN). Some remote workers may feel that this luxury of privacy does not exist on the Internet, but it is indeed possible through a Virtual Private Network. VPN allows remote workers to connect securely over the internet through a private and encrypted network. The benefits of the VPN go beyond trying to bypass region restrictions (GeoBlockers) on your favorite media outlets. Let’s have a look at the top advantages of using a VPN.
End-to-end Data encryption
Through public wi-fi hackers can learn a substantial amount about you and steal some of your credentials. With a VPN you will be able to keep such sensitive data secure. The encryption technology will scramble your data for those trying to sneak a peek on you virtually.
Protected File Sharing
Like through WAN, remote workers will be able to upload files to a shared folder which are exclusively accessible to them.
Remote access
Through VPN remote workers could sent print jobs to the office if needs be and access other hardware remotely as if they were physically by the office.
2. Ironclad Email Security
Despite the popularity of instant messaging platforms even on software used for business. Communication via email doesn’t show any signs of becoming obsolete. In fact, email is essential for remote workers as it’s fast, convenient and you can easily keep track of previous messages sent. Not to mention, it establishes more formality than instant messaging. Unfortunately, emails leave one exposed to certain risks such as:
Email spoofing
Phishing hackers use this method by sending an email with a header or email address seemingly familiar to your remote workers in hopes of misleading them. For example, an email address showing the name of a member of staff or business. Often these emails have misspelling or they use a public email like Gmail ([email protected]).
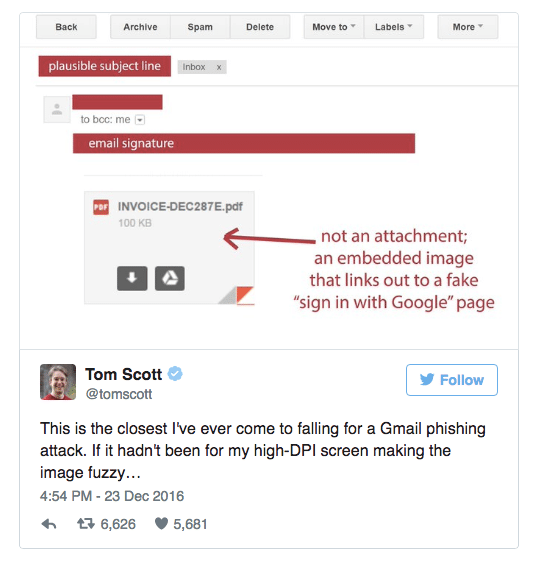
Fake attachments or Phaxattachments
Hackers use a link embedded in an image that looks essentially identical to an email attachment but it’s an URL that prompts users to reveal sensitive information. Could you tell the difference?
Malware attachments
Unlike the phaxattachments, these attachments are truly within the email you receive, but the sender has plans to send you a malicious executable file rather than a harmless pdf. These risks are more easily identifiable as you will be able to see the .exe at the end of such attachments.
So how do you protect yourself and your employees from these phishing attacks?
Be careful about what information you post on your social media.
Social engineering via social media makes it ridiculously easy for phishing hackers to learn certain information about you: where you like to buy your lunch and your mother’s maiden name. They can use this information to seem familiar to you when they do their phishing attacks.
- Be extra cautious around spam email.
- If you are clicking on links, ensure that it is from a reputable source.
- Use a professional and reliable Web Hosting Service.
- In case of doubt forward it to your IT specialist or use an advanced email archiving service.
Use a hosted email service
It is not enough to ask remote workers to be hyper-conscious each time they consult an email. Because let’s be honest, human error can happen from time to time. So, taking extra precautions by using an email hosting service to enhance your protection may not be a bad idea.
This service protects your email through an unbreakable spam guard to fight against phishing attacks. It also performs regular virus scans to identify and eliminate potential risks. Furthermore, it fights against employee’s communicating with unapproved emails while also encrypting emails thus diminishing the risk of data slipping out of your company.
3. SSL Certificate
Remote workers can look if a website has some form of legitimacy by quickly glancing if they possess a SSL certificate. If you see https rather than just http in the address bar, it means there’s an SSL on the web page. Another way to check is by looking for a padlock just left of the URL in the address bar. Clicking on the padlock will bring up additional information on the validity of the SSL certificate.
What is meant by SSL?
SSL or Secure Sockets Layer is technology that safeguards sensitive information of users from hackers intending to modify or look on the personal information being transferred through data encryption.
Benefits of SSL encryption
Protecting Your Business by Protecting your Clients. If your website does require that users provide sensitive information to you, it is essential that you get an SSL certificate to protect the users who will use your website. Because if a hacker acquires information of a client from your site it can result in a loss in patrons and distrust.
SEO benefits of HTTPS
Google wants to protect its users, so they prioritize sites that are more trustworthy. In having an SSL certificate, your website will have HTTPS – secure file transfer. This technology establishes a secure encrypted tunnel for safe communication. Plus, you will stand a better chance of appearing in top SERPs (Search Engine Results Page). This will generate more organic traffic to your site and as a result more sales.
Conclusion
It is much easier to set up an impenetrable defense for cyber-security than to come up with solutions after getting hacked. This tactic helps to discourage cybercriminals rather than encourage them. So, protect yourself, your workers, and your clients by using these proven defense mechanisms.






